Regulation of ESG ratings: after the EU, the United Kingdom is also joining with legislation
British government at the end of October presented to parliament the final version of the law regulating ESG rating providers with an expected effective date from mid‑2028. The legislation will thus follow the steps of the European Union, which plans to enforce specific conditions for rating providers from July 2026.
The European regulation was adopted already at the end of 2024 and aims to ensure that recipients of information, i.e., ESG ratings, have access to transparent information about methodology and assessment, thereby strengthening transparency and independence. Rating providers in the EU are required to obtain authorization from the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) and must provide clear information about the methodology, data and sources used for the assessment.
Difference compared to European legislation
The United Kingdom legislation, similarly to the EU regulation, applies to rating providers based in the United Kingdom as well as to foreign providers operating in the British market. Oversight of the licensing of these activities is entrusted to the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), which, when assessing, intends to focus on four key areas – transparency, governance and management, systems and controls, and conflicts of interest. A more significant difference from the European legislation is to primarily focus on regulating ratings in cases where they are likely to influence investment decisions.
The regulation does not apply to all ESG rating providers
In both European and British legislation, rating providers that operate on a non‑profit basis are excluded from the regulation, such as research and educational institutions, charitable and other non‑profit organisations, or public authorities.
ESG ratings typically provide information about a company's profile in the area of sustainable development and assess the interrelations (impacts or risks) within the E, S and G factors. Among the most well‑known ESG rating providers are, for example, MSCI ESG Rating, Sustainalytics, Refinitiv or Moody’s Analytics.
Sources: Legislation.gov.uk, 2025; FCA, 2025; CMS Law-Now, 2025; EUR-Lex, 2025; EY, 2024
The assessment of ESG factors generally has a significant impact on investors' decision-making, also within supplier‑customer relationships, and ratings are used and in demand. However, the current offering of ratings (including from our experience) suffers primarily from unclear transparency of the methodology and the source data used, which then reduces confidence in the rating result.
Related articles
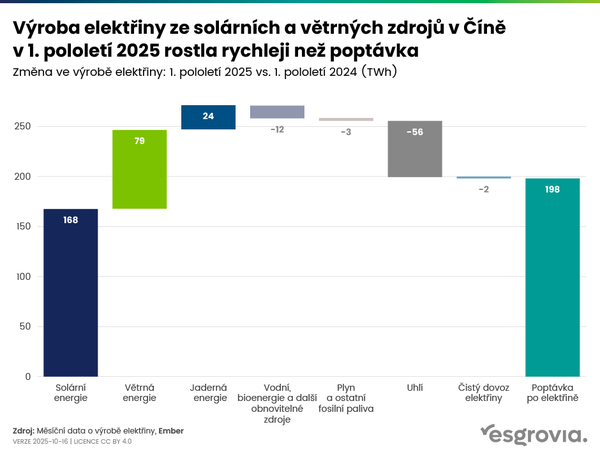
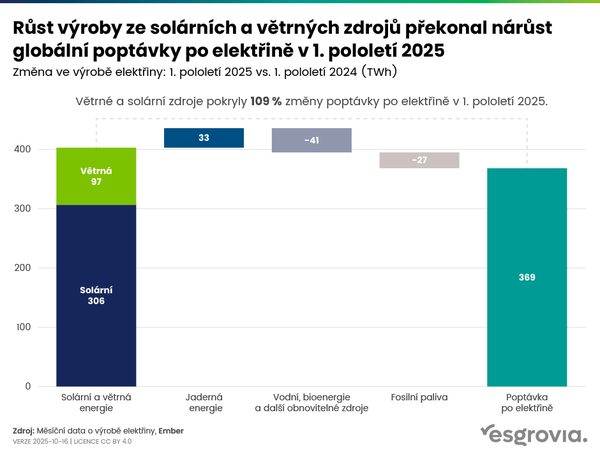
Renewable sources overtook coal as the world's leading source of electricity for the first time
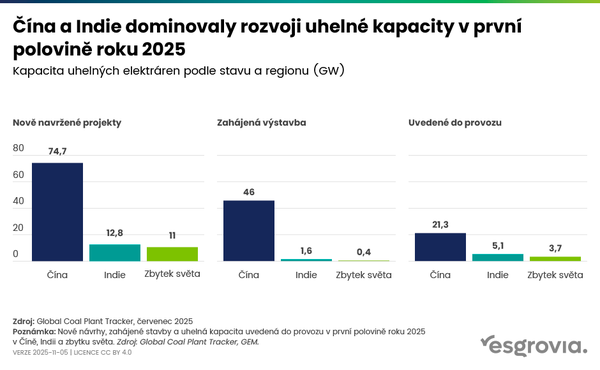
China and India account for 87% of new coal capacity in the first half of 2025
Abundant cheap energy as a determining factor of business sustainability