ESG reporting
ESG reporting means systematic disclosure of non-financial information in the area of a company's sustainable development. The abbreviation ESG comes from the English words Environment, Social and Governance and describes the company's operations and its impacts on the environment, working conditions in the company and the general setting and behavior of the company outward and inward.
"E" as Environment - the basis is the calculation of the carbon footprint, which should be supplemented by other key areas such as water usage, waste production and recycling, or the impact on biodiversity caused by the company's activities.
"S" as Social (work environment and social impacts) - mainly describes labor relations and the level of corporate social responsibility of the company. Main indicators include the development of employee structure, their working conditions, remuneration, or for example training and sickness.
"G" as Governance (company management) - shows the goals and manner of managing the company both internally and externally, including corporate values, transparency, a code of ethics, or relationships with suppliers and customers.
You might be interested in...
What is ESG?
The acronym ESG stands for Environment, Social, and Governance. It describes a company's operations and its impact on the environment, working conditions within the firm, and the general setup and behavior of the company both externally and internally.
Environmental factors include the impacts of an organization's activities on the environment; therefore, aspects such as greenhouse gas emissions, energy and water consumption, waste management, and other connections between the organization's activities and the environment are monitored.
Social factors examine the organization's work environment and all other social impacts. These primarily include the company's relationships with employees, elements of corporate social responsibility, compensation and benefits, diversity or turnover, and other aspects of the relationship between the organization and society.
The term "governance" includes factors essential for managing an organization from a social sustainability perspective. Key elements include transparency, the implementation of ethical and sustainable development values into management, and the ethical management of stakeholder relationships.
ESG elements implemented into company management significantly help managers recognize and improve the organization's influence on its immediate and wider surroundings. They also have a financial impact—companies that act sustainably and socially responsibly generally have a better reputation and thus a better market position.
What is ESG reporting?
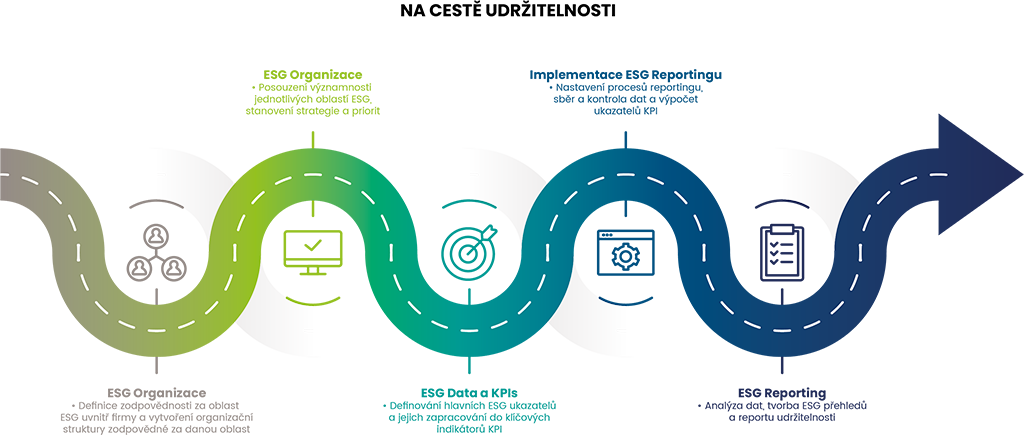
ESG reporting means the systematic disclosure of non-financial information regarding an organization's sustainable development. It involves the regular preparation and publication of a sustainability report, in which the organization describes its progress in key areas of sustainability, i.e., individual E-S-G aspects. An ESG report typically includes a carbon footprint calculation, assessment of other environmental impacts, description of developments and relationships with employees, customers, or shareholders, social responsibility activities, and much more. The report is important not only for external presentation—where investors, financial institutions, employees, and customers are interested in the data—but also enables better internal management through a systematic overview of selected information.
What is an ESG strategy?
The concept of sustainable business should be actively included in the firm's strategic direction, planning, and goals to become an integral part of it. Every organization should therefore create its own sustainable development strategy based on its capabilities. This should include establishing a team responsible for sustainability, defining key ESG areas and integrating them into the company strategy, selecting key indicators, and setting up processes for data collection and the presentation of results internally or in the form of a sustainability report.
Who must publish a sustainability report?
Currently, only a few dozen companies—mostly the largest ones—are required to disclose non-financial data. However, the CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), customers, and banks will compel most medium-sized companies to report on sustainability in the coming years. The CSRD mandates that companies meeting 2 of 3 criteria (minimum 250 employees, turnover of 1 billion CZK, and assets of 500 million CZK) must publish their first non-financial report in 2026 for the previous year. Therefore, information gathering must have started by January 1, 2024 (affecting an estimated 2,000 companies). This obligation will gradually expand to listed small and medium-sized enterprises, which must start collecting data by the beginning of 2025 and reporting from 2026 (with an option to defer). The annual report should be published in a machine-readable format to be stored in a unified European database.
What is an ESG rating?
An ESG rating measures a company's performance in ESG areas and its exposure to ESG risks. ESG ratings are issued by a wide range of agencies; these ratings are not harmonized and can vary in the methodologies used and, consequently, in the final result.
What does ESG investing mean?
It is also referred to as socially responsible investing (SRI), sustainable investing, or impact investing. A typical ESG investor seeks a balance between financial goals (e.g., maximizing Return on Investment - ROI) and ESG parameters. An ESG rating plays a significant role in assessing a company's non-financial parameters and the overall investment.
What is sustainable finance?
Sustainable or green investing, or investing according to ESG criteria, is a form of investment that considers sustainability and social impact alongside financial profit. ESG proponents mainly highlight benefits associated with higher financial performance and lower risk. Beyond aligning financial return maximization with sustainability elements, the long-term goal is to achieve the objectives of the Paris Climate Agreement, which connects financing needs with the reduction of greenhouse gas concentrations.
What are green bonds?
Green bonds are debt securities used to finance projects with a positive impact on the environment and/or climate development. Their purpose is consistent with sustainable development principles, and they also provide a financial advantage, such as tax exemption. Thus, investors can achieve a higher net yield, and they are cheaper for the issuer.
What is the EU Taxonomy?
The EU Taxonomy defines the rules and framework for sustainable development investments that align with the European Green Deal. It is a tool for classifying sustainable economic activities. it works with 6 main objectives: 1. Climate change mitigation, 2. Climate change adaptation, 3. Protection and restoration of biodiversity and ecosystems, 4. Sustainable use and protection of water and marine resources, 5. Pollution prevention and control, and 6. Transition to a circular economy. To comply with the taxonomy, an activity must contribute to at least one of these objectives while doing no significant harm to the others. The investment should also meet minimum safeguards in other business areas—avoiding corruption, child labor, discrimination, etc.
What is the SFDR regulation?
The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) is a set of European rules defining environmentally and socially sustainable activities as economic activities that contribute to environmental protection or social goals. SFDR aims to improve financial market transparency regarding sustainable investments to prevent greenwashing and define rules characterizing sustainable development products.
What does greenwashing mean?
Greenwashing refers to creating and sharing misinformation about the environmental benefits of a product, service, or the operations of an entire company. It is an activity where a company or organization tries to create the impression that it acts ecologically or sustainably when it is not true. Examples include marketing activities that create the illusion of a company being environmentally or socially responsible and meeting rigorous ESG reporting standards, even when the reality is significantly different.
What are ESG funds?
ESG funds focus on investing in companies that emphasize the concept of sustainability alongside financial goals. The aim is to select companies that follow long-term goals and values and, beyond maximizing profit and returns, strive to act ethically, socially responsibly, and ecologically.